Time complexity:
Worst-case: \(O(nlog(n))\)
Best-case: \(O(nlog(n))\)
Average-case: \(O(nlog(n))\)
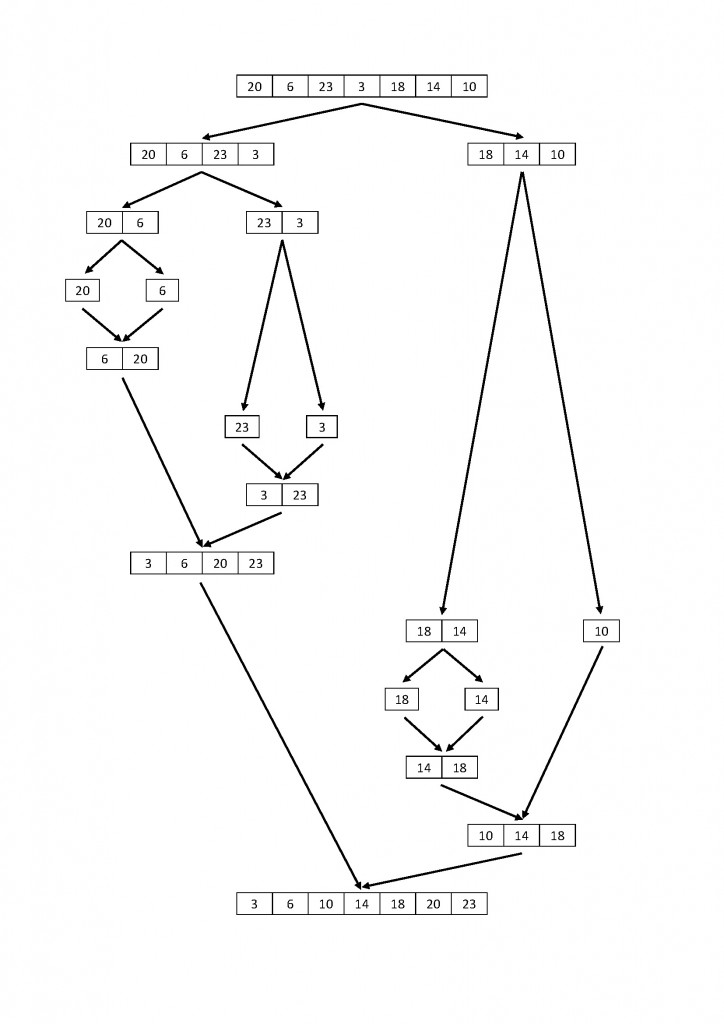
Merge sort divides the array in half, sorts each of those halves, and them merges them back together.
void MergeSort(int *list, int size)
{
partitionStep(list,size, 0, size-1);
}
void mergeStep(int *list, int size, int low, int middle, int high)
{
int i;
int *tmpList = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*size);
for(i=0;i<size;i++)
tmpList[i] = list[i];
int tmpLeft = low;
int tmpRight = middle + 1;
int current = low;
while( (tmpLeft <= middle) && (tmpRight <= high) )
{
if(tmpList[tmpLeft] <= tmpList[tmpRight])
list[current++] = tmpList[tmpLeft++];
else
list[current++] = tmpList[tmpRight++];
}
int remaining = middle - tmpLeft;
for (i=0; i<=remaining; i++)
{
list[current+i] = tmpList[tmpLeft+i];
}
}
void partitionStep(int *list, int size, int low, int high)
{
if(low < high)
{
int i;
int middle = (low + high)/2;
partitionStep(list, size, low, middle);
partitionStep(list, size, middle+1, high);
mergeStep(list, size, low, middle, high);
}
}